High blood pressure or hypertension is a serious medical condition that can go undetected because it often has no symptoms. It’s referred to as “the silent killer” for this reason. High blood pressure can cause heart attacks, strokes, headaches, ruin your kidneys, erectile dysfunction and shrink your brain.
Before you start testosterone replacement TRT, it is very important to get your blood pressure under control. This is done through diet, stress management, lowering your salt intake or the use of blood pressure medications. TRT can increase water retention and blood pressure during the first weeks of treatment. It is a good idea to invest in a home-based blood pressure machine. One usually can be purchased at most pharmacy chains and cost under $ 50. Some, like the OMRON HEM-780, can measure blood pressure easily and keep track of changes with time. Take measurements twice a day until you gain control of your blood pressure again.
Testosterone increases extracellular water ECW. Testosterone acts directly on the kidney, because androgen receptors are expressed in renal tubules. There is evidence that androgens stimulate the expression of the angiotensinogen gene in the kidney, providing a potential mechanism of sodium and water retention by testosterone. This retention can increase weight and blood pressure during the first weeks of TRT. A high proportion of red blood cells (hematocrit) caused by TRT can also increase blood viscosity and blood pressure. High hematocrit can be managed by blood donations.
It is important to have your blood pressure measured during the first month of treatment to ensure that it does not increase with testosterone. The good news is that replacement doses are much less associated with this problem. More serious risks for hypertension are associated with the high testosterone doses associated with performance-enhancing use.
Edema-related swelling is one of TRT’s most troublesome and hard to manage side effects. It can occur to about 20 percent of older patients with comorbidities. The potential causes could be cortisol build up, increase sodium retention, in rare cases high estradiol, or cardiovascular issues..
Most cases of lower extremity (peripheral) edema have nothing to do with estradiol and a lot to do with cardiovascular issues. An important suggestion if edema does not get better after a month on TRT is to get a full cardio workup by a cardiologist.
Some men report decreased edema after a short cycle of a diuretic like HTZ, so that is something to explore. Low sodium intake and plenty of water plus cardio may also help. Cardio exercise and sweating in a sauna have also been reported to help. But these are speculations that should not replace a good cardiovascular work up.
Pulmonary hypertension caused by sleep apnea has also been reported as a cause of edema while on TRT.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Associated with Leg Edema
“A common but under-recognized cause of edema is pulmonary hypertension, which is often associated with sleep apnea. Venous insufficiency is treated with leg elevation, compressive stockings, and sometimes diuretics. The initial treatment of idiopathic edema is spironolactone. Patients who have findings consistent with sleep apnea, such as daytime somnolence, loud snoring, or neck circumference >17 inches, should be evaluated for pulmonary hypertension with an echocardiogram.”
edema[swelling] what is the cause
Ankle swelling after starting testosterone injections
How many of you are on Diuretics for water retention on TRT?
Here are excerpts from an interesting paper:
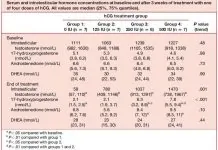
“This is the first controlled study demonstrating that testosterone increases extracellular water (ECW). Previous data concerning the effects of testosterone on plasma volume and urinary sodium excretion are limited and conflicting. The underlying mechanism is unknown, but several possibilities exist. Testosterone could act directly on the kidney because androgen receptors are expressed in renal tubules. There is evidence that androgens stimulate the expression of the angiotensinogen gene in the kidney. Therefore, androgens could activate the local renal RAAS to stimulate sodium and water retention through an autocrine or paracrine mechanism. The epithelial sodium channel plays an important role in the sodium balance, as demonstrated by genetic abnormalities in its activity, such as in Liddle’s syndrome. It has recently been reported that androgens increase mRNA expression of the alpha subunit of the epithelial sodium channel in a human renal cell line, providing a potential mechanism of sodium and water retention by testosterone.
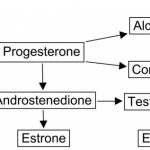
Plasma aldosterone levels fell significantly during testosterone treatment, whereas a modest fall, which failed to reach significance, occurred during GH treatment. During combined treatments, a significant fall in Aldo was also observed. The uniform trend toward a fall in Aldo levels observed with single and combined treatments suggests an adaptive response to ECW expansion. The observation that the fall in Aldo was greater in the presence of testosterone suggests that additional androgen-mediated mechanisms are probably involved. Androgen receptors have been identified in human adrenocortical cells and appear to exert an inhibitory influence. In vitro studies have demonstrated that testosterone reduced the proliferation of human adrenal adenoma and adrenocortical cancer cell lines (38). It is possible that testosterone directly suppresses Aldo biosynthesis or secretion, but this remains to be demonstrated.
More on aldosterone
The effects of testosterone on the volume and distribution of ECW could theoretically occur secondary to aromatization to estrogen in peripheral tissues. Estrogen may cause fluid retention through reduction of the plasma antidiuretic hormone (arginine vasopressin)-plasma osmolality set point (39, 40) or stimulating the synthesis of hepatic angiotensinogen (41), enhancing the overall activity of RAAS and leading to sodium retention. However, this postulate is not supported by the observation that urinary sodium excretion is increased during oral contraceptive use (42) or that the plasma renin concentration is reduced in women receiving estrogen treatment (43). Moreover, estrogen reduces the plasma renin concentration, the activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme, and the Aldo response to angiotensin II. These actions of estrogen putatively generated from aromatization of androgens could explain the slight reduction in plasma Aldo levels in response to testosterone in our study.” Source
Men on TRT notice that they hold more water when they eat higher sodium foods, drink alcohol, and skip the gym for more than 3 days. Higher simple carb intake also worsens water retention. Not drinking enough water also makes the body retain water.
NOTE: Some natural ways to decrease blood pressure are decreasing your salt intake, exercising, keeping a normal body weight for your height, managing stress, and engaging in meditation and yoga. “Erection- friendlier” blood pressure medications like ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors, renin inhibitors, ARB’s (angiotensin II receptor blockers), and combinations of them may be required for men who cannot maintain a blood pressure reading under 130/80 mm Hg. Diuretics, beta blockers, and calcium channel drugs used for hypertension may cause sexual dysfunction in men, but sometimes they cannot be avoided if your blood pressure cannot be controlled with ACE inhibitors or ARBs alone. Bu some studies show that blood pressure medications may be one of the main drug-induced reasons for erectile dysfunction. But managing ED with drugs is a healthier choice than allowing high blood pressure to go untreated due to fears of ED-related side effects. Not only high blood pressure ensure that you have more cardiovascular risks, but it may also negatively affect your kidneys.